C++ SKIA文字绘制
文字绘制主要包括编码转换(主要是中文)、字形解析(点线或image)和实际渲染三个步骤。在这个过程中,字形解析和实际渲染均是耗时步骤。Skia对文字解析的结果做了一套缓存机制。在中文字较多,使用多种字体,绘制的样式(粗/斜体)有变化时,这个缓存会变得很大,因此Skia文字缓存做了内存上的限制。
SkPaint
文字绘制与SkPaint的属性相关很大,先回头看下SkPaint相关的属性
class SkPaint
{
private
SkTypeface* fTypeface;//字体
SkPathEffect* fPathEffect;//路径绘制效果
SkShader* fShader;//取色器
SkXfermode* fXfermode;//混合模式,类似OpenGL里面的Blend设置
SkColorFilter* fColorFilter;//图像绘制时,自定义图像采样函数时使用
SkMaskFilter* fMaskFilter;//路径绘制时,按有无像素做进一步自定义改进处理时使用
SkRasterizer* fRasterizer;//路径绘制时自定义生成像素点的算法时使用
SkDrawLooper* fLooper;//循环绘制,SkCanvas里面的第二重循环,一般不用关注
SkImageFilter* fImageFilter;//SkCanvas的第一重循环,绘制后做后处理用,一般不用关注
SkAnnotation* fAnnotation;//暂时没用到的属性
SkScalar fTextSize;//文字大小
SkScalar fTextScaleX;//文字水平方向上的拉伸,仅用于PDF绘制
SkScalar fTextSkewX;//文字横向扭曲度,仅用于PDF绘制
SkColor fColor;//纯色,在fShader为空时使用
SkScalar fWidth;//带边界时(kStroke_Style/kStrokeAndFill_Style)生效,边界的宽度
SkScalar fMiterLimit;//drawPath时,连接各个path片断时,要求的圆滑连接阈值,Join 类型为默认的kMiter_Join时无效
/*一组不超过32位的属性*/
union {
struct {
// all of these bitfields should add up to 32
unsigned fFlags : 16;//包含所有的0/1二值属性:
/*
kAntiAlias_Flag = 0x01,//是否抗锯齿
kDither_Flag = 0x04,//是否做抖动处理
kUnderlineText_Flag = 0x08,//是否绘制文字下划线
kStrikeThruText_Flag = 0x10,//目前未看到其作用
kFakeBoldText_Flag = 0x20,
kLinearText_Flag = 0x40,
kSubpixelText_Flag = 0x80,//文字像素精确采样
kDevKernText_Flag = 0x100
kLCDRenderText_Flag = 0x200
kEmbeddedBitmapText_Flag = 0x400,
kAutoHinting_Flag = 0x800,
kVerticalText_Flag = 0x1000,//是否竖向绘制文字
kGenA8FromLCD_Flag = 0x2000,
kDistanceFieldTextTEMP_Flag = 0x4000,
kAllFlags = 0xFFFF
*/
unsigned fTextAlign : 2;//文字对齐方式,取值如下:
/*
enum Align {
kLeft_Align,//左对齐
kCenter_Align,//居中
kRight_Align,//右对齐
};
*/
unsigned fCapType : 2;//边界连接类型,分无连接,圆角连接,半方形连接
unsigned fJoinType : 2;//Path片断连接类型
unsigned fStyle : 2;//绘制模式,填充边界/区域
/*
enum Style {
kFill_Style, //填充区域
kStroke_Style,//绘制边界
kStrokeAndFill_Style,//填充区域并绘制边界
};
*/
unsigned fTextEncoding : 2;//文字编码格式,支持如下几种
enum TextEncoding {
kUTF8_TextEncoding,//utf-8,默认格式
kUTF16_TextEncoding,
kUTF32_TextEncoding,
kGlyphID_TextEncoding
};
unsigned fHinting : 2;
unsigned fFilterLevel : 2;//在图像绘制时提到的采样质量要求
//unsigned fFreeBits : 2;
};
uint32_t fBitfields;
};
uint32_t fDirtyBits;//记录哪些属性被改变了,以便更新相关的缓存
}; 字体绘制基本流程
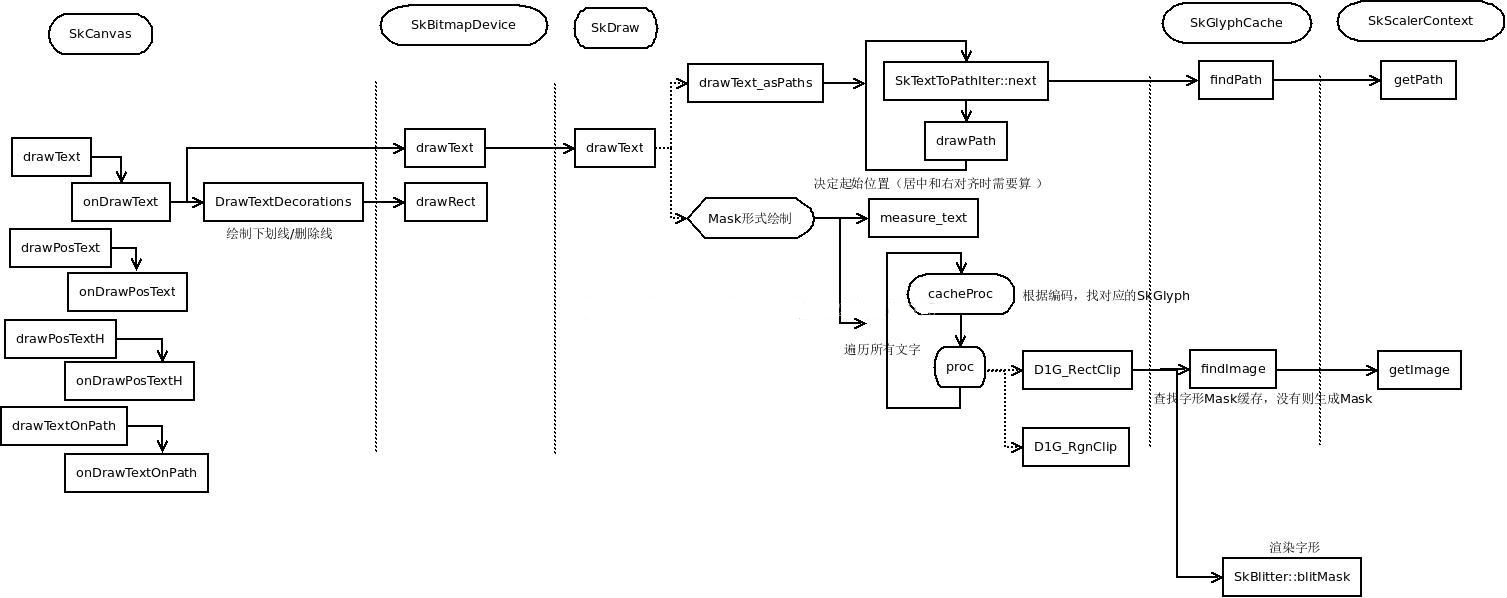
SkCanvas绘制文字和下划线
SkDraw两种绘制方式:
(1)将文字解析为路径,然后绘制路径,缓存路径(drawText_asPaths)。
void SkDraw::drawText_asPaths(const char text[], size_t byteLength,
SkScalar x, SkScalar y,
const SkPaint& paint) const {
SkDEBUGCODE(this->validate();)
SkTextToPathIter iter(text, byteLength, paint, true);
SkMatrix matrix;
matrix.setScale(iter.getPathScale(), iter.getPathScale());
matrix.postTranslate(x, y);
const SkPath* iterPath;
SkScalar xpos, prevXPos = 0;
while (iter.next(&iterPath, &xpos)) {
matrix.postTranslate(xpos - prevXPos, 0);
if (iterPath) {
const SkPaint& pnt = iter.getPaint();
if (fDevice) {
fDevice->drawPath(*this, *iterPath, pnt, &matrix, false);
} else {
this->drawPath(*iterPath, pnt, &matrix, false);
}
}
prevXPos = xpos;
}
} (2)将文字解析为Mask(32*32的A8图片),然后绘制模板,缓存模板。
SkDrawCacheProc glyphCacheProc = paint.getDrawCacheProc();
SkAutoGlyphCache autoCache(paint, &fDevice->fLeakyProperties, fMatrix);
SkGlyphCache* cache = autoCache.getCache();
// transform our starting point
{
SkPoint loc;
fMatrix->mapXY(x, y, &loc);
x = loc.fX;
y = loc.fY;
}
// need to measure first
if (paint.getTextAlign() != SkPaint::kLeft_Align) {
SkVector stop;
measure_text(cache, glyphCacheProc, text, byteLength, &stop);
SkScalar stopX = stop.fX;
SkScalar stopY = stop.fY;
if (paint.getTextAlign() == SkPaint::kCenter_Align) {
stopX = SkScalarHalf(stopX);
stopY = SkScalarHalf(stopY);
}
x -= stopX;
y -= stopY;
}
const char* stop = text + byteLength;
SkAAClipBlitter aaBlitter;
SkAutoBlitterChoose blitterChooser;
SkBlitter* blitter = NULL;
if (needsRasterTextBlit(*this)) {
blitterChooser.choose(*fBitmap, *fMatrix, paint);
blitter = blitterChooser.get();
if (fRC->isAA()) {
aaBlitter.init(blitter, &fRC->aaRgn());
blitter = &aaBlitter;
}
}
SkAutoKern autokern;
SkDraw1Glyph d1g;
SkDraw1Glyph::Proc proc = d1g.init(this, blitter, cache, paint);
SkFixed fxMask = ~0;
SkFixed fyMask = ~0;
if (cache->isSubpixel()) {
SkAxisAlignment baseline = SkComputeAxisAlignmentForHText(*fMatrix);
if (kX_SkAxisAlignment == baseline) {
fyMask = 0;
d1g.fHalfSampleY = SK_FixedHalf;
} else if (kY_SkAxisAlignment == baseline) {
fxMask = 0;
d1g.fHalfSampleX = SK_FixedHalf;
}
}
SkFixed fx = SkScalarToFixed(x) + d1g.fHalfSampleX;
SkFixed fy = SkScalarToFixed(y) + d1g.fHalfSampleY;
while (text < stop) {
const SkGlyph& glyph = glyphCacheProc(cache, &text, fx & fxMask, fy & fyMask);
fx += autokern.adjust(glyph);
if (glyph.fWidth) {
proc(d1g, fx, fy, glyph);
}
fx += glyph.fAdvanceX;
fy += glyph.fAdvanceY;
} cacheProc是翻译字符编码的函数,由SkPaint::getDrawCacheProc产生:
SkDrawCacheProc SkPaint::getDrawCacheProc() const {
static const SkDrawCacheProc gDrawCacheProcs[] = {
sk_getMetrics_utf8_00,
sk_getMetrics_utf16_00,
sk_getMetrics_utf32_00,
sk_getMetrics_glyph_00,
sk_getMetrics_utf8_xy,
sk_getMetrics_utf16_xy,
sk_getMetrics_utf32_xy,
sk_getMetrics_glyph_xy
};
unsigned index = this->getTextEncoding();
if (fFlags & kSubpixelText_Flag) {
index += 4;
}
SkASSERT(index < SK_ARRAY_COUNT(gDrawCacheProcs));
return gDrawCacheProcs[index];
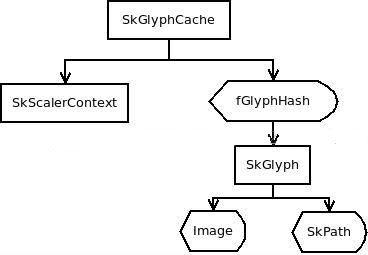
} SkGlyphCache:字形解析的结果缓存。
SkScalerContext:负责字形的解析,有多种实现。Android中是用FreeType:SkScalerContext_FreeType。主要是generateImage和generatePath两个方法:
generateImage:
void SkScalerContext_FreeType::generateImage(const SkGlyph& glyph) {
SkAutoMutexAcquire ac(gFTMutex);
FT_Error err;
if (this->setupSize()) {
goto ERROR;
}
err = FT_Load_Glyph( fFace, glyph.getGlyphID(fBaseGlyphCount), fLoadGlyphFlags);
if (err != 0) {
SkDEBUGF(("SkScalerContext_FreeType::generateImage: FT_Load_Glyph(glyph:%d width:%d height:%d rb:%d flags:%d) returned 0x%x\n",
glyph.getGlyphID(fBaseGlyphCount), glyph.fWidth, glyph.fHeight, glyph.rowBytes(), fLoadGlyphFlags, err));
ERROR:
memset(glyph.fImage, 0, glyph.rowBytes() * glyph.fHeight);
return;
}
emboldenIfNeeded(fFace, fFace->glyph);
generateGlyphImage(fFace, glyph);
}
void SkScalerContext_FreeType_Base::generateGlyphImage(FT_Face face, const SkGlyph& glyph) {
const bool doBGR = SkToBool(fRec.fFlags & SkScalerContext::kLCD_BGROrder_Flag);
const bool doVert = SkToBool(fRec.fFlags & SkScalerContext::kLCD_Vertical_Flag);
switch ( face->glyph->format ) {
case FT_GLYPH_FORMAT_OUTLINE: {
FT_Outline* outline = &face->glyph->outline;
FT_BBox bbox;
FT_Bitmap target;
int dx = 0, dy = 0;
if (fRec.fFlags & SkScalerContext::kSubpixelPositioning_Flag) {
dx = SkFixedToFDot6(glyph.getSubXFixed());
dy = SkFixedToFDot6(glyph.getSubYFixed());
// negate dy since freetype-y-goes-up and skia-y-goes-down
dy = -dy;
}
FT_Outline_Get_CBox(outline, &bbox);
/*
what we really want to do for subpixel is
offset(dx, dy)
compute_bounds
offset(bbox & !63)
but that is two calls to offset, so we do the following, which
achieves the same thing with only one offset call.
*/
FT_Outline_Translate(outline, dx - ((bbox.xMin + dx) & ~63),
dy - ((bbox.yMin + dy) & ~63));
if (SkMask::kLCD16_Format == glyph.fMaskFormat) {
FT_Render_Glyph(face->glyph, doVert ? FT_RENDER_MODE_LCD_V : FT_RENDER_MODE_LCD);
SkMask mask;
glyph.toMask(&mask);
if (fPreBlend.isApplicable()) {
copyFT2LCD16<true>(face->glyph->bitmap, mask, doBGR,
fPreBlend.fR, fPreBlend.fG, fPreBlend.fB);
} else {
copyFT2LCD16<false>(face->glyph->bitmap, mask, doBGR,
fPreBlend.fR, fPreBlend.fG, fPreBlend.fB);
}
} else {
target.width = glyph.fWidth;
target.rows = glyph.fHeight;
target.pitch = glyph.rowBytes();
target.buffer = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(glyph.fImage);
target.pixel_mode = compute_pixel_mode( (SkMask::Format)fRec.fMaskFormat);
target.num_grays = 256;
memset(glyph.fImage, 0, glyph.rowBytes() * glyph.fHeight);
FT_Outline_Get_Bitmap(face->glyph->library, outline, &target);
}
} break;
case FT_GLYPH_FORMAT_BITMAP: {
FT_Pixel_Mode pixel_mode = static_cast<FT_Pixel_Mode>(face->glyph->bitmap.pixel_mode);
SkMask::Format maskFormat = static_cast<SkMask::Format>(glyph.fMaskFormat);
// Assume that the other formats do not exist.
SkASSERT(FT_PIXEL_MODE_MONO == pixel_mode ||
FT_PIXEL_MODE_GRAY == pixel_mode ||
FT_PIXEL_MODE_BGRA == pixel_mode);
// These are the only formats this ScalerContext should request.
SkASSERT(SkMask::kBW_Format == maskFormat ||
SkMask::kA8_Format == maskFormat ||
SkMask::kARGB32_Format == maskFormat ||
SkMask::kLCD16_Format == maskFormat);
if (fRec.fFlags & SkScalerContext::kEmbolden_Flag &&
!(face->style_flags & FT_STYLE_FLAG_BOLD))
{
FT_GlyphSlot_Own_Bitmap(face->glyph);
FT_Bitmap_Embolden(face->glyph->library, &face->glyph->bitmap,
kBitmapEmboldenStrength, 0);
}
// If no scaling needed, directly copy glyph bitmap.
if (glyph.fWidth == face->glyph->bitmap.width &&
glyph.fHeight == face->glyph->bitmap.rows &&
glyph.fTop == -face->glyph->bitmap_top &&
glyph.fLeft == face->glyph->bitmap_left)
{
SkMask dstMask;
glyph.toMask(&dstMask);
copyFTBitmap(face->glyph->bitmap, dstMask);
break;
}
// Otherwise, scale the bitmap.
// Copy the FT_Bitmap into an SkBitmap (either A8 or ARGB)
SkBitmap unscaledBitmap;
unscaledBitmap.allocPixels(SkImageInfo::Make(face->glyph->bitmap.width,
face->glyph->bitmap.rows,
SkColorType_for_FTPixelMode(pixel_mode),
kPremul_SkAlphaType));
SkMask unscaledBitmapAlias;
unscaledBitmapAlias.fImage = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(unscaledBitmap.getPixels());
unscaledBitmapAlias.fBounds.set(0, 0, unscaledBitmap.width(), unscaledBitmap.height());
unscaledBitmapAlias.fRowBytes = unscaledBitmap.rowBytes();
unscaledBitmapAlias.fFormat = SkMaskFormat_for_SkColorType(unscaledBitmap.colorType());
copyFTBitmap(face->glyph->bitmap, unscaledBitmapAlias);
// Wrap the glyph's mask in a bitmap, unless the glyph's mask is BW or LCD.
// BW requires an A8 target for resizing, which can then be down sampled.
// LCD should use a 4x A8 target, which will then be down sampled.
// For simplicity, LCD uses A8 and is replicated.
int bitmapRowBytes = 0;
if (SkMask::kBW_Format != maskFormat && SkMask::kLCD16_Format != maskFormat) {
bitmapRowBytes = glyph.rowBytes();
}
SkBitmap dstBitmap;
dstBitmap.setInfo(SkImageInfo::Make(glyph.fWidth, glyph.fHeight,
SkColorType_for_SkMaskFormat(maskFormat),
kPremul_SkAlphaType),
bitmapRowBytes);
if (SkMask::kBW_Format == maskFormat || SkMask::kLCD16_Format == maskFormat) {
dstBitmap.allocPixels();
} else {
dstBitmap.setPixels(glyph.fImage);
}
// Scale unscaledBitmap into dstBitmap.
SkCanvas canvas(dstBitmap);
canvas.clear(SK_ColorTRANSPARENT);
canvas.scale(SkIntToScalar(glyph.fWidth) / SkIntToScalar(face->glyph->bitmap.width),
SkIntToScalar(glyph.fHeight) / SkIntToScalar(face->glyph->bitmap.rows));
SkPaint paint;
paint.setFilterLevel(SkPaint::kMedium_FilterLevel);
canvas.drawBitmap(unscaledBitmap, 0, 0, &paint);
// If the destination is BW or LCD, convert from A8.
if (SkMask::kBW_Format == maskFormat) {
// Copy the A8 dstBitmap into the A1 glyph.fImage.
SkMask dstMask;
glyph.toMask(&dstMask);
packA8ToA1(dstMask, dstBitmap.getAddr8(0, 0), dstBitmap.rowBytes());
} else if (SkMask::kLCD16_Format == maskFormat) {
// Copy the A8 dstBitmap into the LCD16 glyph.fImage.
uint8_t* src = dstBitmap.getAddr8(0, 0);
uint16_t* dst = reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*>(glyph.fImage);
for (int y = dstBitmap.height(); y --> 0;) {
for (int x = 0; x < dstBitmap.width(); ++x) {
dst[x] = grayToRGB16(src[x]);
}
dst = (uint16_t*)((char*)dst + glyph.rowBytes());
src += dstBitmap.rowBytes();
}
}
} break;
default:
SkDEBUGFAIL("unknown glyph format");
memset(glyph.fImage, 0, glyph.rowBytes() * glyph.fHeight);
return;
}
// We used to always do this pre-USE_COLOR_LUMINANCE, but with colorlum,
// it is optional
#if defined(SK_GAMMA_APPLY_TO_A8)
if (SkMask::kA8_Format == glyph.fMaskFormat && fPreBlend.isApplicable()) {
uint8_t* SK_RESTRICT dst = (uint8_t*)glyph.fImage;
unsigned rowBytes = glyph.rowBytes();
for (int y = glyph.fHeight - 1; y >= 0; --y) {
for (int x = glyph.fWidth - 1; x >= 0; --x) {
dst[x] = fPreBlend.fG[dst[x]];
}
dst += rowBytes;
}
}
#endif
} generatePath:
void SkScalerContext_FreeType::generatePath(const SkGlyph& glyph,
SkPath* path) {
SkAutoMutexAcquire ac(gFTMutex);
SkASSERT(&glyph && path);
if (this->setupSize()) {
path->reset();
return;
}
uint32_t flags = fLoadGlyphFlags;
flags |= FT_LOAD_NO_BITMAP; // ignore embedded bitmaps so we're sure to get the outline
flags &= ~FT_LOAD_RENDER; // don't scan convert (we just want the outline)
FT_Error err = FT_Load_Glyph( fFace, glyph.getGlyphID(fBaseGlyphCount), flags);
if (err != 0) {
SkDEBUGF(("SkScalerContext_FreeType::generatePath: FT_Load_Glyph(glyph:%d flags:%d) returned 0x%x\n",
glyph.getGlyphID(fBaseGlyphCount), flags, err));
path->reset();
return;
}
emboldenIfNeeded(fFace, fFace->glyph);
generateGlyphPath(fFace, path);
// The path's origin from FreeType is always the horizontal layout origin.
// Offset the path so that it is relative to the vertical origin if needed.
if (fRec.fFlags & SkScalerContext::kVertical_Flag) {
FT_Vector vector;
vector.x = fFace->glyph->metrics.vertBearingX - fFace->glyph->metrics.horiBearingX;
vector.y = -fFace->glyph->metrics.vertBearingY - fFace->glyph->metrics.horiBearingY;
FT_Vector_Transform(&vector, &fMatrix22);
path->offset(SkFDot6ToScalar(vector.x), -SkFDot6ToScalar(vector.y));
}
} 字体缓存管理
SkTypeface是Skia中的字体类,对应可有多种字体库解析实现。
SkTypeface 记录一个字体的id,在使用时,到链表中查出相关的字体。
对一个字体和样式,建一个 SkGlyphCache缓存,内含一个 SkScalerContext 和一个 SkGlyph 的哈希表,SkGlyph 缓存一个字体中一个字解析出来的位图。此有内存容量限制,当超过容量时,会清除之前缓存的位图。Hash冲突时,直接生成新字形替换原来的字形。
缓存限制的内存宏详见:src/core/SkGlyphCache_Globals.h。和include/core/SkUserConfig.h中的SK_DEFAULT_FONT_CACHE_LIMIT宏
struct SkGlyph {
void* fImage;
SkPath* fPath;
SkFixed fAdvanceX, fAdvanceY;
uint32_t fID;
uint16_t fWidth, fHeight;
int16_t fTop, fLeft;
void* fDistanceField;
uint8_t fMaskFormat;
int8_t fRsbDelta, fLsbDelta; // used by auto-kerning
}; 当绘制字体只绘边界或者位图缓存机制不好处理时,将字体解析成点线,构成SkPath,也做缓存。